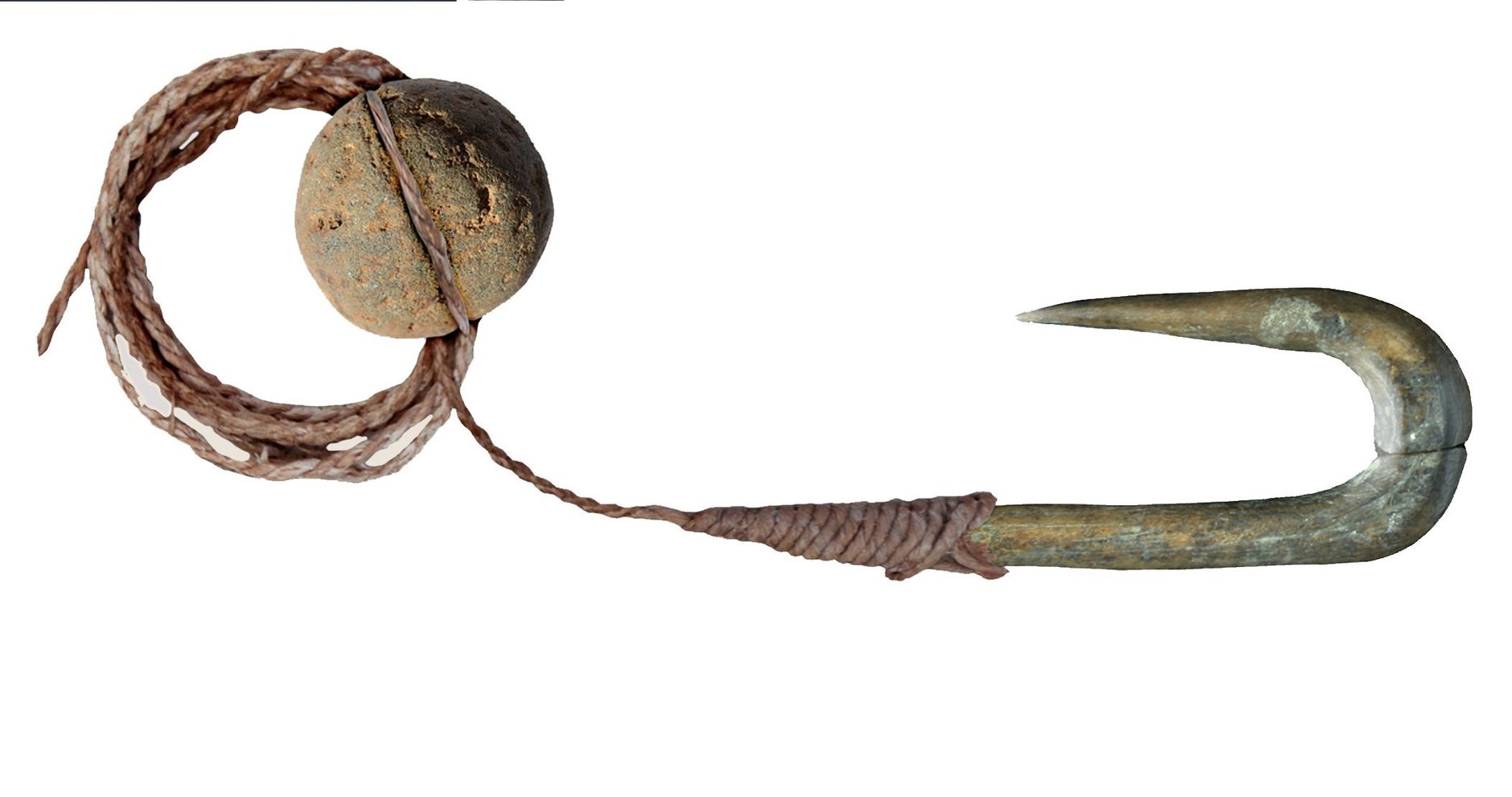
(CN) — A collection of 19 bone fish hooks and six grooved pebbles suggests that prehistoric anglers had a detailed knowledge of fish behavior and diet as early as 13,000 years ago and likely used some of the same fishing techniques used today.
The hooks and pebbles — believed to have been used as sinkers — were found at the archaeological site called the Jordan River Dureijat, located on the banks of the Jordan River in northern Israel and dates back to the Epipaleolithic period, according to a study published Wednesday in the journal PLOS ONE. It’s some of the earliest evidence of complex fishing technology.
Fish remains have been found at sites inhabited by human ancestors dating back to nearly 2 million years. But studying what technology early humans used to acquire fish is difficult because fishing gear was typically made from perishable materials like wood and plant fibers, and they’re only preserved in unusual conditions.
The waterlogged Jordan River Dureijat site was discovered in 1999 as a result of a drainage operation. But back in the Levantine Epipaleolithic periods, it was a short-term encampment that was intermittently occupied over a span of about 10,000 years, according to an earlier study published in the PaleoAnthropology journal. It was never used for habitation, but rather it was a place that people repeatedly visited to fish and hunt and take advantage of other natural resources.
In addition to the fish hooks and pebbles — the largest collection of early fishing technology to be found — arrowheads and limestone axes have also been found at the site. And because the site has been covered in water, tiny rodent and fish bones are well-preserved.
In Wednesday’s study, a team of archeologists – led by Antonella Pedergnana of the Archaeological Research Centre and Museum for Human Behavioural Evolution in Mainz, Germany – found plant residue on the hooks and stones that indicate the use of fishing line.
They also found a wide variety of hook shapes, suggesting they were used for catching a variety of fish sizes, and grooved lines and fiber residues on some hooks indicate the use of artificial lures.
“A look at the [the Jordan River Dureijat] fishing gear reveals that all fishing techniques and knowledge already existed some 13,000 years ago,” the study’s authors wrote in a statement.
The innovations coincide with the beginning of the transition to agriculture, and the use of lures and a wide variety of hook shapes “suggests the humans of this time were not only hunting a broad spectrum of fish, but also that they had profound knowledge of fish behavior and ecology,” researchers note.
Based on the size of the hooks and their grooves and the remains of captured fish at the site, researchers estimate the lines used in fishing were likely strong enough to pull a 2-pound, “and possibly even heavier,” fish out of the water, according to the study.
But the hooks don’t have any eyes or holes in the shank through which to thread the line, something researchers note was likely because it weakened the narrow shank. Instead, they have grooves or knobs on the shaft, and traces of wear indicate the line wasn’t connected by a single twist but by a “complex method of binding, wrapping and tying.”
Archeologists also found residual evidence of an adhesive being used to secure the line.
The use of artificial bait was confirmed by the presence of deep grooves, adhesives and animal hair on the end of two hooks. These lures may have included “shell flutters,” or pieces of shiny mother-of-pearl that spin in the water and attract fish.
Modern anglers still use shiny lures today, and the use of light-weight lures are used with specific casting techniques, such as fly fishing.
“Given the small dimensions of the hooks likely to have been equipped with artificial lures at [Jordan River Dureijat], the possibility that a similar angling method was already in use during the Natufian [era] should not be ruled out,” the study authors note.
“Except for the use of metal and plastic, modern fishing has not invented anything new since the Natufian,” they added in a statement.
Subscribe to Closing Arguments
Sign up for new weekly newsletter Closing Arguments to get the latest about ongoing trials, major litigation and hot cases and rulings in courthouses around the U.S. and the world.